Balmoral Software
Solutions: 1
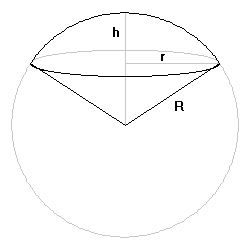
A spherical cone consists of a spherical cap surmounting an inverted cone of the same lateral extent whose apex is at the center of the associated sphere. There is exactly one equable spherical cone.
Define the following notation:
R: Radius of the sphereThe volume of the spherical cone is V, where
h: Height of the spherical cap, 0 < h < R
r: Radius of the widest part, 0 < r < R
V/π = (2/3)R2hThe lateral surface area of the upper portion is Scap, where
Scap/π = 2RhThe lateral surface area of the lower portion is Scone, where
Scone/π = RrThe above three quantities are integers by convention. Then
V/π = (R/3)(2Rh) = (R/3)(Scap/π),so
is rational. We have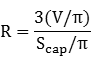
r2 = R2 - (R - h)2 = 2Rh - h2The equability requirement is
The spherical cone cannot be equable if R ≤ 3, so assume R > 3 and square both sides: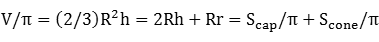
2h(R - 3) = 3r
4h2(R - 3)2 = 9r2 = 9(2Rh - h2)The coefficient of h is strictly positive and we can thus solve for h:h[4(R - 3)2 + 9] = 18R
Since R is rational, so is h. We then have
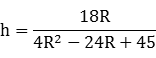
[1]
The fractional part at right has a positive numerator since R > 3. Its denominator was previously established to also be positive, so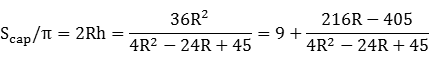
A solution for R requires that the discriminant of this quadratic be non-negative: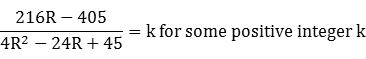
4kR2 - 24(k + 9)R + 45(k + 9) = 0 [2]
We can then evaluate [3] to see which of the 36 possible values of k produces a square discriminant, as required by a rational solution for R in [2]. There is only one such value, and the corresponding roots for R are checked for R > 3, and in [1] to see if a valid value of h in the range 0 < h < R is produced:
Discriminant = 576(k + 9)2 - 720k(k + 9) ≥ 0 [3] 1 ≤ k ≤ 36
The single solution is a sphere with radius 5 and cap height 18/5, for which the volume and surface area are equal to 60 π:
k Discriminant Quadratic in R [2] Roots for R h 27 2162 108R2 - 864R + 1620 = 0 3 (discard), 5 18/5
R = 5
h = 18/5
r = 24/5
Scap = 36 π
Scone = 24 π
V = 60 π
Copyright © 2019 Balmoral Software (http://www.balmoralsoftware.com). All rights reserved.